Liebe Leser,
in diesem Beitrag werden Sie Wichtiges über weißen Hautkrebs erfahren.
Weißer Hautkrebs bezieht sich auf eine Gruppe von Hautkrebsarten, die hauptsächlich aufgrund der Exposition gegenüber UV-Strahlen auftreten. Dazu gehören Basalzellkarzinom (Basaliom) und Plattenepithelkarzinom (Spinaliom). Diese Krebsarten sind in der Regel weniger aggressiv als das maligne Melanom, können aber dennoch ernste Folgen haben, wenn sie nicht frühzeitig erkannt und behandelt werden.
Basalzellkarzinome machen den Großteil der Fälle von weißem Hautkrebs aus. Sie entstehen in den Basalzellen der Haut und neigen dazu, langsam zu wachsen. Plattenepithelkarzinome entwickeln sich aus den oberflächlichen Hautschichten und können sich schneller ausbreiten als Basaliome.
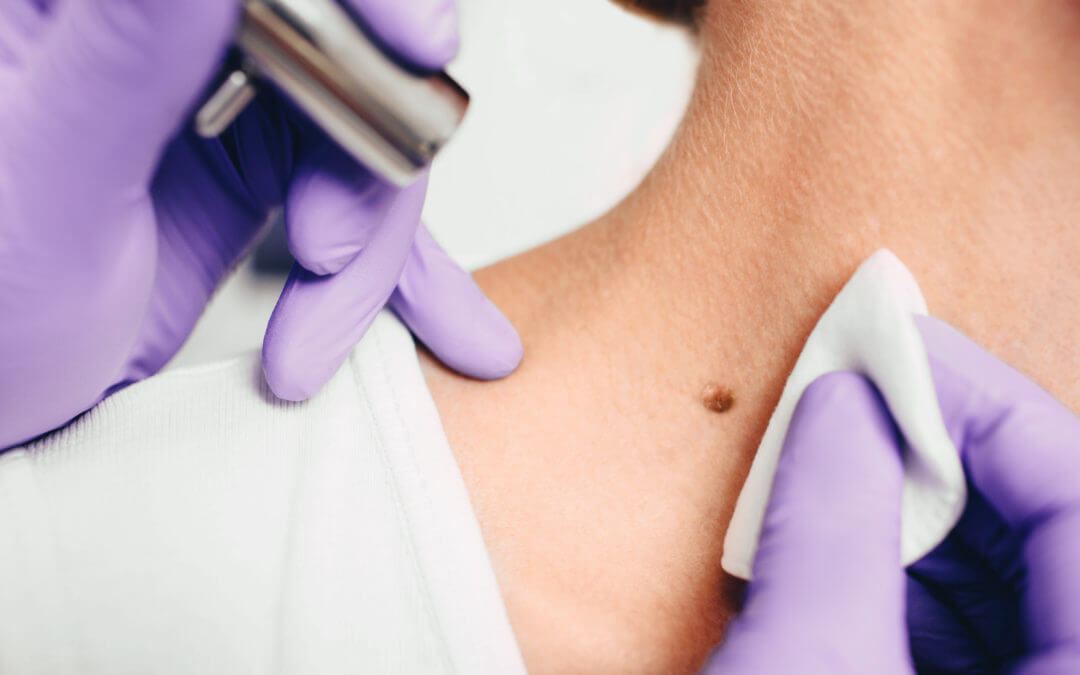
Zu den Risikofaktoren für weißen Hautkrebs gehören übermäßige Sonneneinstrahlung, insbesondere bei Menschen mit heller Haut sowie häufige Sonnenbrände in der Kindheit oder Jugend. Regelmäßige Hautuntersuchungen sind wichtig, um verdächtige Hautveränderungen frühzeitig zu erkennen und zu behandeln.
Die Behandlung von weißem Hautkrebs, insbesondere von Basalzellkarzinomen und Plattenepithelkarzinomen, hängt von verschiedenen Faktoren ab, darunter die Art und Größe des Tumors, seine Lage auf der Haut sowie der Gesundheitszustand des Patienten. Im Allgemeinen gibt es mehrere Optionen für die Behandlung von weißem Hautkrebs:
- Chirurgische Entfernung: Dies ist oft die erste Wahl bei kleinen Tumoren. Der Arzt entfernt den Krebs und einen kleinen Rand gesunder Haut, um sicherzustellen, dass alle Krebszellen entfernt wurden.
- Mohs-Chirurgie: Dies ist eine spezielle Technik, bei der der Tumor schichtweise entfernt und sofort untersucht wird, um sicherzustellen, dass alle Krebszellen entfernt wurden. Mohs-Chirurgie wird häufig bei Tumoren im Gesicht oder anderen sensiblen Bereichen angewendet.
- Kryotherapie: Hierbei wird der Tumor durch Einfrieren mit flüssigem Stickstoff zerstört. Dies wird typischerweise für kleinere Basaliome oder Spinaliome verwendet.
- Elektrochirurgie: Bei diesem Verfahren werden Krebszellen mithilfe elektrischer Energie entfernt.
- Strahlentherapie: Diese kann eingesetzt werden, wenn eine Operation nicht möglich ist oder wenn der Krebs sich ausgebreitet hat.
- Medikamentöse Therapien: In einigen Fällen können topische Medikamente wie Imiquimod oder Fluorouracil verwendet werden, um Hautkrebszellen zu zerstören.
Die Wahl der Behandlung hängt von der individuellen Situation ab und wird in der Regel von einem Dermatologen oder Onkologen festgelegt. Es ist wichtig, dass Patienten regelmäßige Hautuntersuchungen durchführen lassen und verdächtige Hautveränderungen ihrem Arzt melden, um Hautkrebs frühzeitig zu erkennen und zu behandeln.
Für weitere Fragen zu dem weißen Hautkrebs sprechen Sie mich gerne direkt an oder vereinbaren Sie einen Termin entweder telefonisch oder online über Jameda https://dr-u-falk.de/online-termine/.


Neueste Kommentare